Microsoft Azure Integration
The Azure deployment types integrate CloudShell with the Microsoft Azure public cloud. This integration enables the deployment of CloudShell Apps in Microsoft Azure. CloudShell supports deploying Azure virtual machines from Azure Marketplace images and Azure custom images.
CloudShell supports two integration methods with Azure - "on prem" and "cloud". In "on prem", CloudShell Server is already installed locally and requires a VPN connection to Azure, while in "cloud", CloudShell needs to be installed on the Azure region along with the CloudShell integration resources. For details about the "cloud" method, see Integrating Azure with Cloud-based CloudShell Installation.
The following diagram illustrates an Azure integration (with a local CloudShell installation) hosting two live sandboxes:
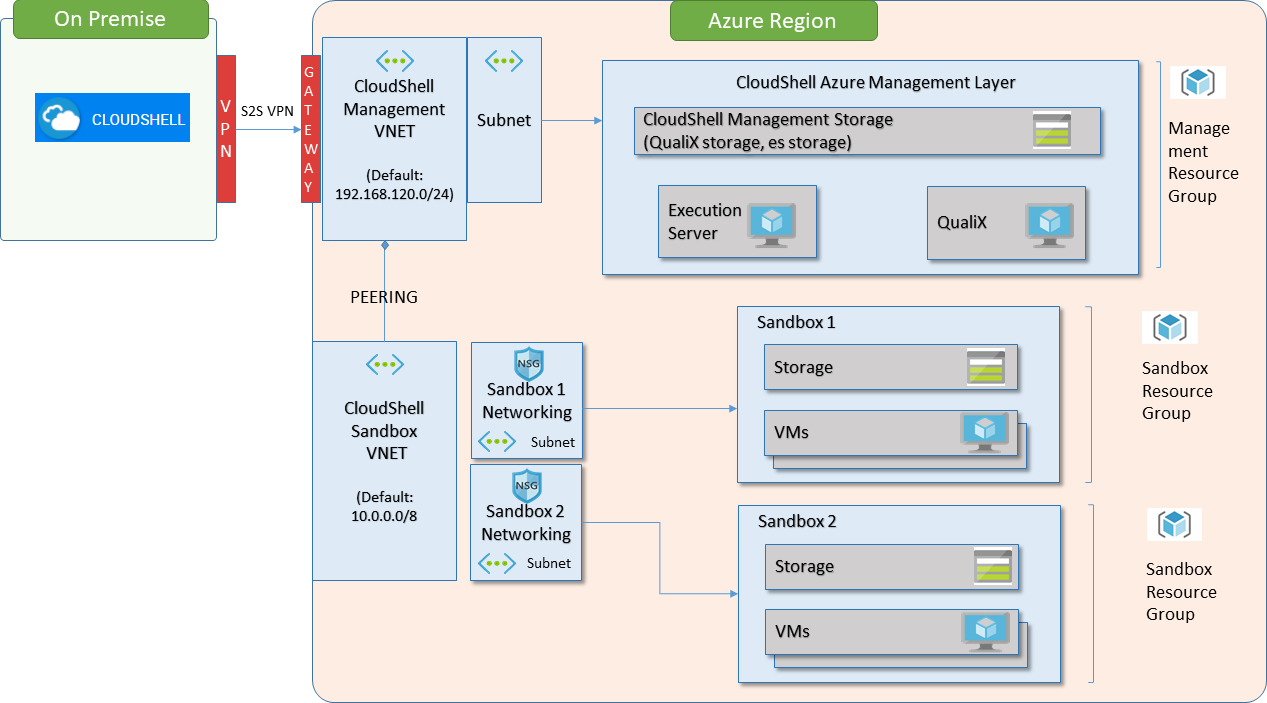
The deployment architecture in Azure requires a management resource group to be created for each relevant Azure region (all Azure regions are supported by CloudShell). This resource group has two virtual networks (VNets):
- CloudShell-Management-VNet: VNet containing two Azure virtual machines, which are always on:
Execution-Server-VM: Execution Server to be used to deploy and manage the Azure virtual machines, and run scripts and commands on them.
The Execution Server in the CloudShell Management VNet needs to access the Quali Server, which is located outside of the CloudShell Management VNet (on-premise, another Azure VNet or another public cloud). To allow this access, you need to configure a VPN between the CloudShell Management VNet and the network in which the Quali Server resides.
- QualiX-VM: QualiX Server used to enable in-browser connections, such as RDP, Telnet and SSH access to Apps in the sandbox
- CloudShell-Sandbox-VNet: VNet containing a subnet for each CloudShell sandbox, which hosts all Azure App virtual machines created within the sandbox and allows them to communicate with each other. The CloudShell Management VNet’s QualiX Server and Execution Server have access both to this VNet and each virtual machine's operating system to run commands and installations on the sandboxes.
Note: Keeping Azure resources, like the CloudShell Management VNet's virtual machines, running at all times entails a fixed monthly rate.
When a new CloudShell sandbox with Azure Apps is starting, the out-of-the-box setup process creates a new subnet for the sandbox within the CloudShell Sandbox VNet. This VNet is connected to the CloudShell Management VNet using a VNet Peering connection. All Azure Apps within the same sandbox are deployed in this sandbox subnet (within the CloudShell Sandbox VNet), and a dedicated Azure resource group is created for each sandbox to hold all Azure resources related to that sandbox. This architecture allows both QualiX Server and the Execution Server to access the Apps in the sandbox while keeping the Apps within one sandbox isolated from Apps in other sandboxes.
- Azure virtual machines in the same sandbox live in the same subnet and can interact with each other.
- CloudShell allows sandboxes to have multiple subnets. If multiple subnets are defined (in the blueprint), the setup process will create the defined subnet networks instead of the default subnet. For additional information, see Subnet Connectivity.
- When the sandbox ends, all related Azure resources, including the sandbox subnet, resource group and virtual machines are automatically deleted by CloudShell.
Azure installation workflow
For each Azure region you want to integrate with CloudShell, perform the following steps:
