VLAN Connectivity
CloudShell provides dedicated VLAN services that enable the creation of Layer 2 connections between both physical and virtual endpoints (for example, physical servers and App-deployed virtual machines) by allocating a VLAN ID for each connection. VLAN-based connectivity supports both peer-to-peer and many-to-many connections.
To use VLANs in CloudShell, the system administrator needs to perform the following configurations:
- Make sure the organization's L2 switches are properly modeled in CloudShell, and include the appropriate resource connections, as explained in Define the Resource Connections of the Switch or Patch Panel.
- Associate the VLAN service family to the domain categories
- Customize the VLAN service models
Tip: CloudShell supports connecting vCenter Apps to existing port groups. For details, see Connecting vCenter Apps to an existing VLAN port group.
How CloudShell creates VLAN connections
When resolving a VLAN connection between sandbox resources/Apps, CloudShell assumes the devices can access one another on the L2 network. In other words, if the connection involves several interconnected switches, CloudShell only configures the edges of the layer 2 networks but doesn’t affect what happens inside.
For example, the diagram below illustrates an L2 network using three L2 switches. Switch 1 is connected to your physical devices, while switches 2 and 3 comprise the fabric.
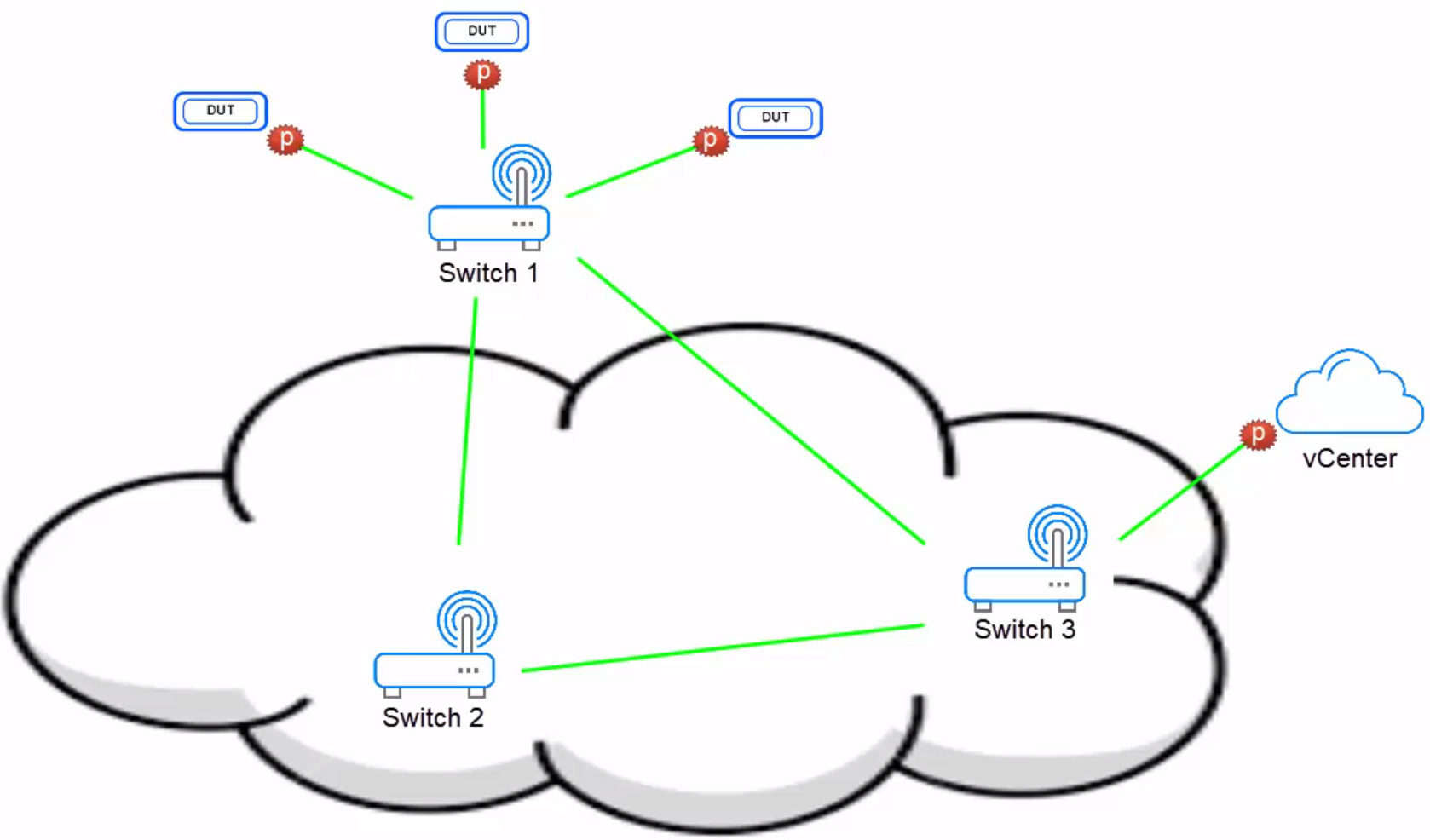
When connecting any of the endpoints, whether its physical devices or virtual machines deployed in your vCenter server, CloudShell only cares about their immediate ports, and not what happens between them.
How CloudShell allocates VLAN IDs
CloudShell allocates VLAN IDs for routes using several parameters that are defined by the administrator in the VLAN service. The parameters are Pool Name, VLAN ID, Allocation Ranges, and Isolation Level, which are explained below.
CloudShell can check availability for a specific VLAN ID or find an available VLAN ID within the defined Allocation Ranges.
When connecting a route that uses a VLAN service, CloudShell allocates the VLAN ID based on the availability of the VLAN ID in the pool specified, which is the domain by default. However, if the VLAN ID is Shared (defined in the Isolation Level attribute), it can be shared among multiple connections in the same sandbox and between sandboxes in the same domain/pool.
Associate the VLAN service family to the domain categories
To expose the VLAN services in the Apps / Services catalog of a specific domain, you must associate the service family to each desirable domain's service category. For information about creating service categories for domains, see Creating a service catalog category.
To associate the VLAN services to the domain category:
- As system administrator, log into Resource Manager Client.
-
In the Admin ribbon, click Resource Families.
The Resource Families explorer is displayed.
-
Click the service family containing the VLAN services. For example, Virtual Network.
The family's Parameters pane is displayed.
- Click the Categories tab.
-
Click Add.
The Select Category dialog box is displayed.
- Select the domain category. To select multiple categories, press the [Shift] key.
- Save your changes.
Customize the VLAN service models
This section explains how to customize the default settings of the VLAN service and control which settings can be changed by the user in the blueprint diagram. To learn how to add a VLAN service to a blueprint and set the service's attribute values, see Services in Blueprints.
Note: Additional VLAN services can be created. For example, you could set up multiple VLAN Auto services in the same domain, each with a different allocation range. Simply duplicate an existing VLAN service and edit the settings, as appropriate. Then, in the Scripts - Resource management page, add the new VLAN service model to the Vlan Service Connect All script.
-
VLAN Auto: This preset automatically selects the VLAN ID for each endpoint connection out of a defined range according to availability in the domain's pool. VLAN Auto allocates VLAN IDs as exclusive by default. This means that the same VLAN ID cannot be used in two or more sandboxes in the same pool.
Note: VLAN Auto selects only one available VLAN ID, even if it is used in Trunk mode.
 Customizing a VLAN Auto preset
Customizing a VLAN Auto preset
To customize a VLAN Auto preset's attributes:
-
In the Resource Families explorer, open the Virtual Network service family and click the VLAN Auto service model. Alternatively, copy the service model to customize a separate preset.
The Parameters pane is displayed to the right of the Resource Families explorer.
-
Click the Attributes tab and configure the required attributes:
Attribute Description Access Mode Determines if the VLAN is configured as Access or Trunk. Default is Access.
Note: Only Access mode is supported for OpenStack instances deployed in CloudShell sandboxes.
Allocation Ranges Determines the ranges of VLAN IDs that can be used. CloudShell will select the first available ID from the allocation ranges specified.
You can specify one or more ranges, and specific VLAN IDs. Multiple values are separated by a comma. Default range is 2-4094 for VLAN and 16777216 for VXLAN.
For example: "3, 100-220, 300-350"
Note: VXLAN ID ranges are only supported for OpenStack cloud provider. To use VXLAN IDs, the VLAN service must be connected to a virtual endpoint that supports VXLAN. VXLAN IDs are supported only for OpenStack.
Important: Modifying a range will not affect VLANs that are currently in use.
Isolation Level Determines if the allocated VLAN ID is Exclusive or Shared. Default is Exclusive. Virtual Network Read only field that stores the allocated VLAN ID. This can be published for users to see but cannot be edited. VLAN ID (Optional) Enables you to specify the VLAN ID (or range if Access Mode is set to Trunk) to use. The VLAN ID must be included in the specified allocation range. However, if the VLAN ID is already allocated exclusively to someone else, an error will be displayed. Pool Name (Optional) Enables you to specify a value to be used as the pool name. This is especially useful for CloudShell configurations that involve multiple domains in different geographic sites.
If empty, the domain name is used.
Note: A VLAN service can allocate the same VLAN in different domains if the pool name is not set.
QinQ (Only in Access mode) Sets the VLAN connection to be in QinQ mode. This requires the L2 switch device to support QinQ. Default is False.
Note: If QinQ mode is enabled on the VLAN service but cannot be established on the L2 switch (for example, because it is not supported on the switch or disabled on the port to be used), the connection will fail.
- Save your changes.
-
-
VLAN Manual: This preset enables the user to specify the VLAN ID to use. VLAN Manual allocates VLAN IDs as shared by default.
 Customizing a VLAN Manual preset
Customizing a VLAN Manual preset
To customize a VLAN Manual preset's attributes:
-
In the Resource Families explorer, open the Virtual Network service family and click the VLAN Manual service model. Alternatively, copy the service model to customize a separate preset.
The Parameters pane is displayed to the right of the Resource Families explorer.
-
Click the Attributes tab and configure the required attributes:
Access Mode Determines if the VLAN is configured as Access or Trunk. Default is Access.
Note: Only Access mode is supported for OpenStack instances deployed in CloudShell sandboxes.
Isolation Level Determines if the allocated VLAN ID is Exclusive or Shared. Default is Shared. Virtual Network Read only field that stores the allocated VLAN ID. This can be published for users to see but cannot be edited. VLAN ID (Mandatory) Enables you to specify the VLAN ID (or range if Access Mode is set to Trunk) to use. If the VLAN ID is already allocated exclusively to someone else, an error will be displayed. Pool Name (Optional) Enables you to specify a value to be used as the pool name. This is especially useful for CloudShell configurations that involve multiple domains in different geographic sites.
If empty, the domain name is used.
Note: A VLAN service can allocate the same VLAN in different domains if the pool name is not set.
QinQ (Only in Access mode) Sets the VLAN connection to be in QinQ mode. This requires the L2 switch device to support QinQ. Default is False.
Note: If QinQ mode is enabled on the VLAN service but cannot be established on the L2 switch (for example, because it is not supported on the switch or disabled on the port to be used), the connection will fail.
- Save your changes.
-
-
P2P VLAN Default: This preset enables you to set the default VLAN settings to be used by peer-to-peer connections. By default, it allocates an exclusive VLAN ID for each endpoint connection out of a defined range according to availability in the domain's pool.
 Customizing a P2P VLAN Default preset
Customizing a P2P VLAN Default preset
The default VLAN service to be used for peer-to-peer connections can be defined by a P2P VLAN Default service model. Even if not configured, a peer-to-peer fallback is provided by CloudShell, as described in the note at the bottom of this section.
Note: P2P VLAN Default is an admin-level service that is only visible to domain and system administrators in CloudShell Portal.
To customize a P2P VLAN Default preset's attributes:
-
In the Resource Families explorer, open the Virtual Network - Administrative service family and click the P2P VLAN Default service model. Alternatively, copy the service model to customize a separate preset.
The Parameters pane is displayed to the right of the Resource Families explorer.
-
Click the Attributes tab and configure the required attributes:
Access Mode Determines if the VLAN is configured as Access or Trunk. Default is Access.
Note: Only Access mode is supported for OpenStack instances deployed in CloudShell sandboxes.
Allocation Ranges Determines the ranges of VLAN IDs that can be used. CloudShell will select the first available ID from the allocation ranges specified.
You can specify one or more ranges, and specific VLAN IDs. Multiple values are separated by a comma. Default range is 2-4094 for VLAN and 16777216 for VXLAN.
For example: "3, 100-220, 300-350"
Note: VXLAN ID ranges are only supported for OpenStack cloud provider. To use VXLAN IDs, the VLAN service must be connected to a virtual endpoint that supports VXLAN. VXLAN IDs are supported only for OpenStack.
Important: Modifying a range will not affect VLANs that are currently in use.
Isolation Level Determines if the allocated VLAN ID is Exclusive or Shared. Default is Exclusive. Virtual Network Read only field that stores the allocated VLAN ID. This can be published for users to see but cannot be edited. VLAN ID (Optional) Enables you to specify the VLAN ID (or range if Access Mode is set to Trunk) to use. The VLAN ID must be included in the specified allocation range. However, if the VLAN ID is already allocated exclusively to someone else, an error will be displayed. Default VLAN Defines the Virtual Network service as a default service to use for peer-to-peer connections.
Pool Name (Optional) Enables you to specify a value to be used as the pool name. This is especially useful for CloudShell configurations that involve multiple domains in different geographic sites.
If empty, the domain name is used.
Note: A VLAN service can allocate the same VLAN in different domains if the pool name is not set.
QinQ (Only in Access mode) Sets the VLAN connection to be in QinQ mode. This requires the L2 switch device to support QinQ. Default is False.
Note: If QinQ mode is enabled on the VLAN service but cannot be established on the L2 switch (for example, because it is not supported on the switch or disabled on the port to be used), the connection will fail.
-
Save your changes.
Notes: When a peer-to-peer connection is being resolved, CloudShell selects a VLAN to use according to the following logic:- CloudShell selects the P2P VLAN Default service that exists in the blueprint.
- Otherwise, it uses a P2P VLAN Default service in a category associated to the user's domain.
- Otherwise, it uses a P2P VLAN Default service in CloudShell.
- Otherwise, the VLAN Auto preset's settings are used.
Related Topics
-
