Managing Public Cloud Apps in Domains
The procedures in this article apply to Apps hosted on a public cloud provider, like AWS EC2 or Azure. For private cloud Apps like vCenter, see Managing Private Cloud Apps in Domains.
CloudShell does not support the deployment of public cloud Apps on different cloud regions in the same sandbox. It is therefore required to include (in a blueprint or sandbox) only Apps with an active deployment path that is associated to a single cloud provider resource. A warning is displayed if this design guideline is not kept.
In this process, you will configure the App's deployments to be carried out by the execution server(s) installed on the public cloud provider's region. This is done by associating the cloud provider and App to the domain, and associating the appropriate execution server to the cloud provider resource and to the shell that defines the deployed App. Technically, this requires specifying a value in the execution server's Execution Server Selector attribute, and setting that value in the cloud provider resource and deployed App shell. Note that resource association to a domain makes sure that users use cloud providers allocated to their domains, while assigning the Execution Server Selector ensures that the actual drivers will run next to the cloud provider to reduce latency and improve performance.
CloudShell supports two public cloud providers out-of-the-box, AWS EC2 and Azure. In AWS EC2, we use two execution servers: es-shells deploys the instances on AWS and therefore needs to be associated to the cloud provider resource, and es-commands runs scripts and commands on the AWS instances and needs to be associated to the shell of the deployed Apps. In Azure, since the authentication mechanism works a bit differently, we use one execution server called Execution-Server-VM that needs to be associated to both the cloud provider resource and deployed App shell.
For illustration purposes, we will configure an AWS App in this article.
This is a five step process:
- Decide which CloudShell domain to associate to the public cloud region
- Set the execution server's selector attribute
- Create a cloud provider resource in the required domain
- Configure the Execution Server to support Ansible operations
- Associate the public cloud App to the domain
Important: Before you begin, make sure CloudShell has been configured on the required public cloud region. See AWS Integration or Microsoft Azure Integration.
Set the execution server's selector attribute
This procedure explains how to prepare the execution server to deploy the Apps. The Execution Server Selector attribute must have the Execution Server Selector rule enabled.
To associate an execution server to the domain:
-
In CloudShell Portal, click Manage.
The Manage dashboard is displayed.
-
In the left sidebar, click Execution Servers.
-
In the left pane, under Execution Servers, click Servers.
The execution server list is displayed.
-
Click the name of the appropriate execution server. Note that this execution server is installed on the cloud provider itself.
The Attributes dialog box is displayed.
-
Select the Execution Server Selector check box and specify a value. For example, ES1:
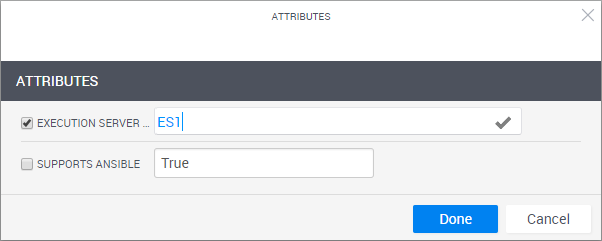
For AWS EC2 Apps, perform these steps twice, once for the es-shells execution server and again for the es-commands execution. Specify a different value on each execution server. For illustration purposes, we'll set "ES1" as the value on es-shells and "ES2" as the value on es-commands.
- Click Done.
- Repeat these steps to associate additional execution servers to the domain.
Create a cloud provider resource in the required domain
To set the cloud provider resource to the domain:
- As system administrator, log in to CloudShell and select the required domain.
-
Create the cloud provider resource, as explained in Adding AWS EC2 Cloud Provider Resource and Adding Microsoft Azure Cloud Provider Resource.
-
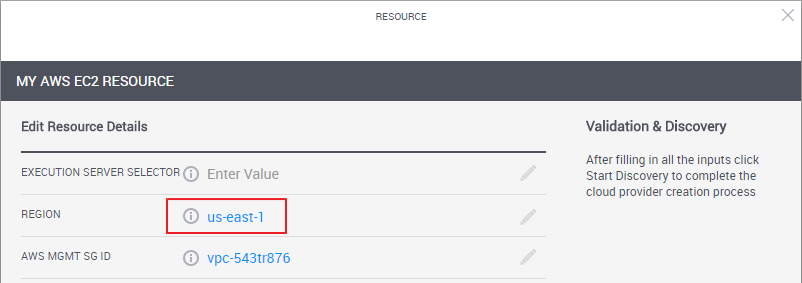
In the Region attribute, enter the public cloud's region that is relevant for the current domain.
For example, AWS EC2 resource with a Region selected:
- In the Execution Server Selector attribute, specify the value you set in the Execution Server Selector attribute on the appropriate execution server (es-shells for AWS ES2 - "ES1" in our case).
- Complete the resource creation process.
Configure the Execution Server to support Ansible operations
Note: This section is only required for Ansible configuration management.
To use Ansible to install and configure applications on Apps, the system administrator needs to perform several configurations on the Linux-based Execution Server that will be used to run the Ansible operations on the App's deployed VMs. For additional information, see Ansible Playbook Development for Apps.
Associate the public cloud App to the domain
To make the App available to members of specific domains, in the App template, select the cloud provider resource with the required region and associate the domain categories to the App.
To associate an App to a domain:
-
In the Manage dashboard, in the left sidebar, click Apps.
The Apps page is displayed.
-
Create a new App or edit an existing one, as explained in Managing App Templates.
The App's configuration wizard is displayed.
-
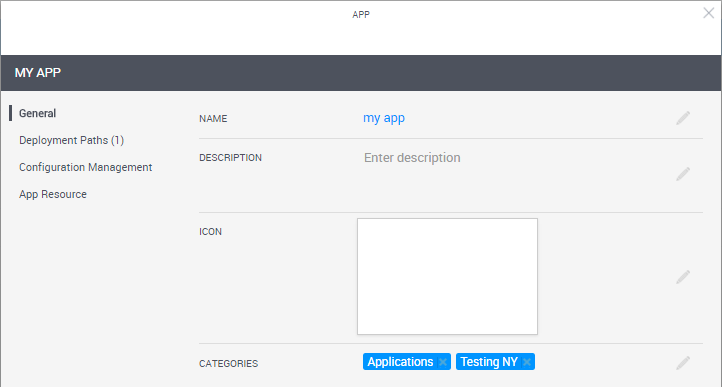
To make the App available to members of this domain, from the Categories dropdown list, select the categories associated to the domain. For details about creating domain categories, see Managing domain categories.
For example, Testing NY:
- If this is a new App, in the Deployment Paths page, create a deployment path for the cloud provider. Make sure to select the cloud provider resource you created in the required CloudShell domain.
-
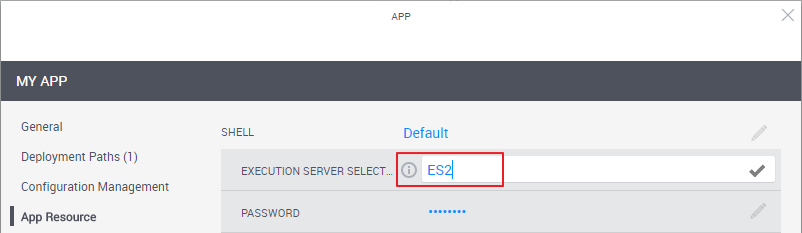
In the App Resource page, in the Execution Server Selector attribute, specify the value you set in the Execution Server Selector attribute on the appropriate Execution Server. For AWS EC2 Apps that have a custom shell driver, specify the value on the es-commands Execution Server ("ES2" in our case).
Note: If the Execution Server Selector attribute is missing, ask the system administrator to associate it with the deployed App's resource model in Resource Manager Client. By default, the Generic App Model model is used.
- Click Done.
Related Topics