L1 Switches
CloudShell includes dedicated specialized features for working with L1 switches. These are implemented using CloudShell Shells. To learn how to use L1 switches in CloudShell Portal, see L1 switches in CloudShell Portal.
This article explains how to update an L1 switch with a new shell. For details specific to a particular L1 switch, see the documentation set included with the switch's shell.
Why update an L1 switch?
Every major CloudShell release includes updated resource configurations for the different L1 switches. After upgrading to a new L1 version, you should import the updated shells for that device in your lab. The shell includes the family, model, attributes, and driver.
The steps for updating an L1 switch are as follows:
- Import an L1 shell to CloudShell using the instructions in this article.
- Create the L1 switch resource
- Update the L1 switch firmware, if needed.
- Sync between the L1 switch and CloudShell to load the switch's blades, ports, and settings.
- Define the resource connections of the L1 switch
- (Optional) Configure L1 switch runtime and replace any incompatible mappings.
- Set the timeout period for L1 drivers, if needed.
Verify user privileges
To deploy an L1 shell, make sure you have the following permissions:
- User with Administrator privileges for Resource Manager Client
- Username and password for the L1 switch
Import an L1 shell to CloudShell
An updated shell may add new options, while rendering others obsolete. Check the release notes for instructions on managing changed functionality.
Note: To support physical endpoints, make sure your physical switches and routers use shells compatible with your version of CloudShell.
To import an L1 Shell:
-
Download the shell to a temporary location. See Quali Repositories.
Tip: Before you import, open the zip file and verify that it includes an install_driver.bat file. If it doesn't include this file, download this older version of CloudShell Help and follow the import procedure in the L1 Switches article.
-
Copy the shell to the Quali Server’s \Drivers installation folder.
If the folder is missing, create it in the Server installation directory. By default: C:\Program Files (x86)\QualiSystems\CloudShell\Server\Drivers.
-
Extract the shell’s zip file here. Make sure the .exe and .json files are located directly under the \Drivers folder.
-
In command-line, navigate to the extracted folder and run the install_driver.bat file.
When the process completes, return to the Drivers folder and make sure you see an .exe file for the shell.
-
Make sure the L1 shell's .exe file is unblocked.
- Right-click the file and select Properties.
- If you see an Unblock option, select it and click OK.
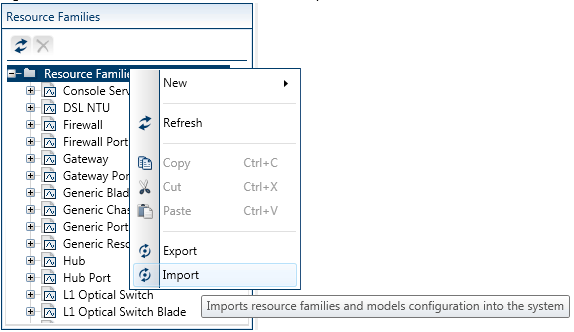
- In Resource Manager Client, open the Admin ribbon, and click Resource Families.
- In the Resource Families explorer, right-click the root and select Import.
- Navigate to the shell’s download folder, open the data model folder, select the ...ResourceConfiguration.xml file and click Open.
-
In the confirmation window, click OK.
The driver, families and resource models of the L1 switch are added to CloudShell.
-
Optionally refresh the Resource Families explorer to see the new L1 switch families and models.
Note: There is no need to restart Quali Server to complete this procedure.
- If you are upgrading an existing Layer 1 shell, stop all existing processes of this shell that have the same name as the shell's .exe files included in the shell’s downloaded folder.
Create the L1 switch resource
To create an L1 switch resource:
- In Resource Manager Client, open Resource Explorer.
- Add a new Folder that will house the L1 switch resources.
-
Right-click the folder and select New>Resource.
The New Resource dialog box is displayed.
-
Enter a Name for the resource.
Note: The resource's name has a limit of 100 characters and can only contain alpha-numeric characters, spaces, and the following characters: | . - _ ] [
-
Enter the device's Address.
If you are creating a resource for an OnPath switch on Horizon, make sure the address includes the Horizon server's address and the name of the OnPath. For example, "192.168.10.214?Horizon=OnPath1" where 192.168.10.214 is the Horizon server's address and OnPath1 is the name of the OnPath.
-
Select the switch's Family, Model and Driver.
Note: The updated Family, Model and Drivers are added when you import the shell to Resource Manager Client. The driver contains the device's relevant commands, enables connectivity, and enables you to autoload/syncronize the switch with the updated settings. More about autoload and synchronizations in Sync between the L1 switch and CloudShell.
- Click OK.
-
-
In Resource Explorer, right-click the new resource and select Configuration.
The resource's Configuration tab is displayed.
- Enter the switch's User and Password access credentials.
- Save your changes.
Update the L1 switch firmware
Drivers are designed to work with a limited range of firmware. Updating a driver may require you to update the L1 switch's firmware as well, and vice-versa. Make sure a compatible driver is available before updating the L1 switch's firmware.
Sync between the L1 switch and CloudShell
To sync between the L1 switch and CloudShell:
-
If you are configuring an L1 switch for the first time or if the device's structure has changed, use the Auto Load operation to create the resource structure of the resource in CloudShell, along with the switch's settings.
If the resource was previously autoloaded, Auto Load will update the resource's structure and attributes to match the switch. This includes creating missing sub resources, removing sub resources that are missing from the device, replacing sub resources that are using the wrong model with the correct ones, and also copying mappings and attributes from the switch.
Additional options include Sync From and Sync To:
- The Sync From operation updates the attributes of the CloudShell resource but does not override the resource structure like the Auto Load operation. Sync From updates attributes such as software version, switch address, port names and alarm states with the existing settings of the switch.
-
The Sync To operation enables you to update the physical device's settings with the settings defined in the CloudShell resource. To change the values of specific attributes on the physical device, in the Settings document of the resource, edit the attribute values and click Activate.
Note: Sync From and Sync To can also be performed on a specific sub-resource, such as a blade or a port, while Auto Load applies to the entire resource structure. For additional information about these operations, see Inventory Drivers and Utilities.
-
Set port attributes.
The resource configuration for a switch model includes default attributes and value sets for each type of switch.
Significant attributes for using the switch in a blueprint route include:
- Protocol - a read-write attribute allows users to determine the protocol to be used by the port
- Protocol Type - used to mark a port as Ethernet or Fibre channel
- Speed - a read-write attribute that determines the transmission speed or rate for the port
Admin users can modify the switch attributes and values in CloudShell and apply the new values to the device, but in most cases, an L1 switch allows a list of permitted protocols and speeds for its ports.
Typically, the L1 switch is set as a shared resource that is available to multiple users while the L1 switch ports are set as exclusive per sandbox. If the protocol type and speed attributes are associated with the switch ports, each user can specify which connectivity settings to use for the selected ports.
If protocol type and speed are not specified, the route uses the default protocol type and speed for the switch.
- Next, if you need to make adjustments to the port mappings (for example, to replace incompatible mappings), manually modify the ports and mappings and apply the changes to the device.
Define the resource connections of the L1 switch
For detailed information on how to do this, see Define the Resource Connections of the Switch or Patch Panel.
Configure L1 switch runtime
Switch runtime behavior is determined by a combination of settings in the driver's runtime configuration file and the values set for the port attributes. Each driver includes a runtime configuration that stores login information, logging preferences, and default actions to perform.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Runtime_Configuration>
<Host Address="Default">
<Attribute Name="VERBOSE" Step="INFORM" Value="5" />
<Attribute Name="::CommonDriver_CTRL::Address" Step="INIT" Value="192.168.41.198" />
<Attribute Name="::CommonDriver_CTRL::User" Step="INIT" Value="admin" />
<Attribute Name="::CommonDriver_CTRL::Password" Step="INIT" Value="pxc***" />
</Host>
<Host Address="192.168.42.240">
<Attribute Name="VERBOSE" Step="INFORM" Value="5" />
</Host>
</Runtime_Configuration>
To change logging preferences:
- Navigate to the Shell’s server folder, select the ... RuntimeConfig.xml file and click Open.
-
Edit the
VERBOSEkey for each host.Verbose values range from 1, which documents only critical errors, to 7, which documents every action the driver takes. High verbosity creates large log files and can affect the time taken to resolve switch commands.
- Save the file.
Set the timeout period for L1 drivers
CloudShell manages the execution of L1 resource commands using a dedicated process for each L1 driver on the Quali Server machine. The process is named after the driver and is created when running the first command of an L1 driver in the sandbox, after restarting Quali Server or if the driver's previous process was terminated during the sandbox's lifecycle.
However, some drivers, especially Python-based drivers, may require a longer startup time than the default 2 seconds timeout period defined in CloudShell. If the driver does not respond within the defined period, the following error message is displayed: "No response received from agent".
To set a different timeout period for L1 drivers:
- Open the C:\Program Files (x86)\QualiSystems\CloudShell\Server\customer.config file, add the following key, and set the value in seconds:
<add key="L1DriverProcessStartupTime" value="3"/> - Restart the Quali Server service.
L1 switches in CloudShell Portal
This section applies to both patch panels and L1 switches. For brevity, the term "L1 device" is used for both.
When you reserve a blueprint that has resources with connectivity requirements, CloudShell will resolve those connections using the L1 device resource(s) you configured.
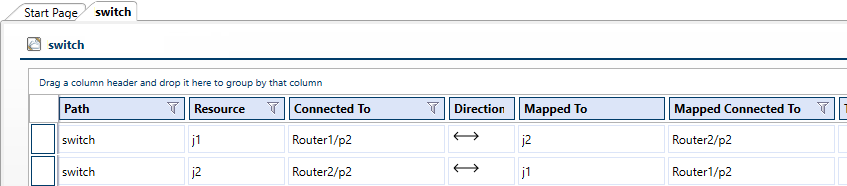
Note: You can see an L1 device's resolved connections in real time in the Resource Explorer. Right-click the L1 device resource and select Settings. In the L1 resource's Settings tab, click the Mappings button. For example, a switch that connects the "Router2" and "Router1" resources to each other:
CloudShell Portal also enables you to reserve specific blades/ports for the duration of the sandbox. You can either drag the L1 resource into the sandbox (its default is shared) and then use the Add sub resources option to add some ports to the diagram (this will allocate the ports exclusively to sandboxes based on this blueprint), or you can use the Unshare option on the L1 device resource itself to get exclusive access to the entire resource for that sandbox.
To learn how to add sub-resources and unshare a resource, see Configure Sub-resources and Share Reserved Resources.
