Configure the Linux Execution Server
The steps described in this section need to be applied only once. The only mandatory values that are required for the configuration of the Execution Server (ES) are:
- TeamMachine
- Username
- Password
-
Execution Server Name
Note: For Ansible configuration management, the /ansible flag needs to be enabled. See Example: How to Run the Configuration File.
However, you can optionally use other configuration parameters that are provided. You can use their default values or modify them. You may use as many of the configuration parameters as needed.
To display the usage of the QsExecutionServerConsoleConfig.exe file, in command-prompt, navigate to the /root/ExecutionServer folder (or opt/ExecutionServer for Linux machines on Azure or AWS) and enter it at the command prompt, as depicted in the following image:
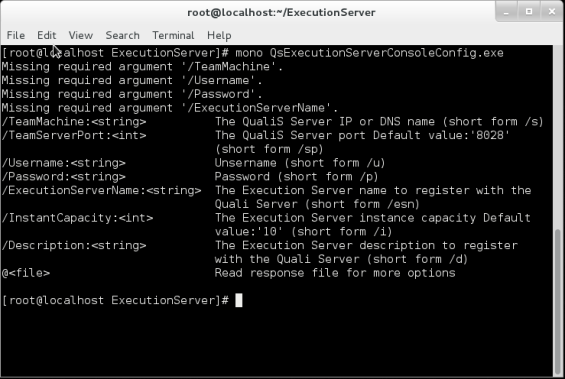
Each of these parameters has a short form as well. For example:
mono QsExecutionServerConsoleConfig.exe /s:192.168.1.66 /u:admin /p:admin /esn:my-exec- To install the Linux Execution Server in an offline environment, make sure the OfflinePackageRepository zip file is extracted to the local PyPi Server repository. For details, see Add the out-of-the-box dependencies package to the local PyPi Server repository.
-
Quali Server must be running when configuring the Execution Server.
- For TeamMachine, specify the Quali Server's private IP or DNS name.
- Python drivers and scripts run on the Python installation that is provided by CloudShell at: /usr/local/bin/python.
- Depending on your flavor of Linux, you may need to escape parameter values containing special characters with single or double quotes. For example:
"admin1234!" - Suite execution is not available for Linux Execution Servers.
- The CloudShell admin's credentials are specified in plain text. You can remove the credentials to enhance security. For details, see Execution Servers.
Useful commands
To change the command slot capacity:
-
Edit the Linux Execution's installation script at /etc/systemd/system/es.service.
-
Change the command slot capacity. For example
ES_NUMBER_OF_SLOTS=10 -
Save the file.
-
Reload and restart the service.
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadsudo systemctl restart es
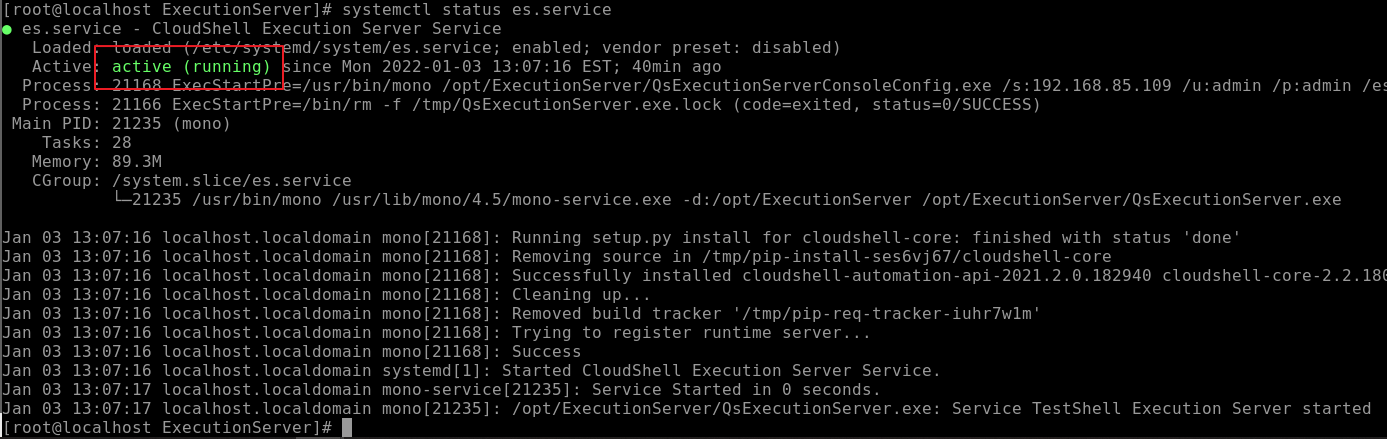
To verify the service status:
sudo systemctl status es.serviceAnd make sure it is "active (running)":
To restart the service:
sudo systemctl restart esTo view installation logs and other useful information:
sudo cat /var/log/messagesTo view these logs in real time:
sudo tail -f /var/log/messages