Add an OpenStack App Template
The App template defines the settings and configurations of the VM to be deployed in the sandbox as well as the application(s) to be installed on that VM.
To add a new OpenStack App template:
-
Click + Add.
The Create New App wizard is displayed.
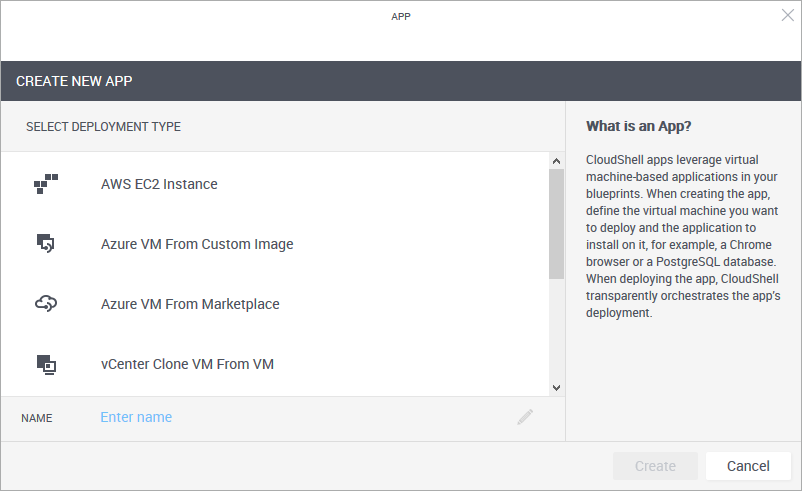
- From the Select Deployment Type pane, select OpenStack Deploy From Glance Image.
-
Enter a Name for the App template.
Note: The App template's name has a limit of 100 characters and can only contain alpha-numeric characters, spaces, and the following characters: | . - _ ] [
-
Click Create.
The App template is created and the App wizard's General page is displayed.
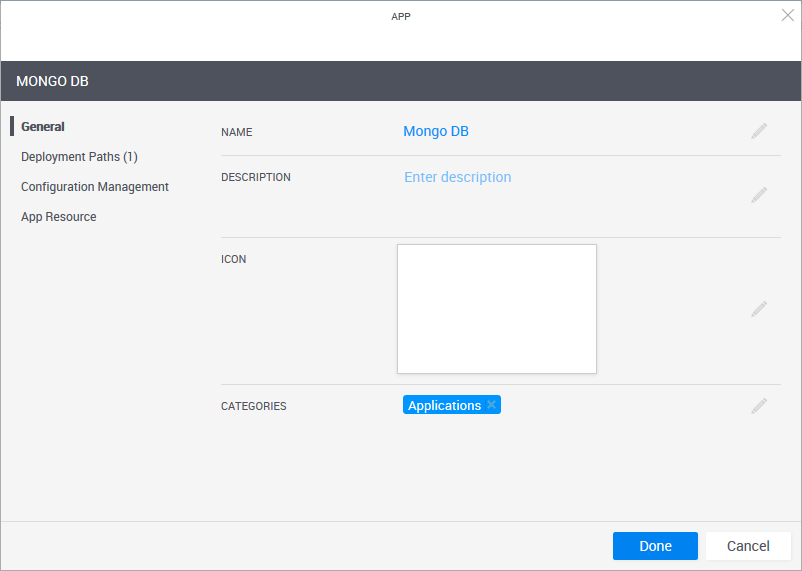
-
In the General page, define the App template's display settings and category.
 More...
More...
Field Required Description Name Required App name that is displayed in the catalog. Description Optional Description of the App. Icon Optional Add an image to the catalog definition. The recommended size for the image is 190x120 pixels (image size is limited to 400x400 pixels or 200 KB). Categories Optional Service categories are a method to classify Apps. The Apps are displayed in the Add App / Service side pane in the blueprint and sandbox diagram, arranged in categories. Only users who are permitted to view the category can access the App. Apps without a category are not displayed.
By default, the Applications category is selected.
Select a category from the dropdown list. You can select additional categories. Examples of categories are: applications, networking and VLAN.
Notes:- The category must be associated with the domain in which the required cloud provider resides. For information about domain categories, see Managing domain categories.
- It is recommended to use up to a 2-level hierarchy when organizing the Add App / Service catalog (i.e. root and sub-category).
- In the Add App / Service side pane, Apps are displayed in the root category only. This includes services associated to sub-categories.
-
In the left pane, click Deployment Paths and configure the App template's deployment path.
 More...
More...
A deployment path define(1) the OpenStack Glance image, (the method to be used to deploy the VM), (2) the VM’s settings such as storage size, CPU and image file, and (3) the CloudShell cloud provider resource that enables CloudShell to access the cloud provider and deploy the VM on it.
Note the deployment path's name (highlighted in the image below). The path's name is dynamic and consists of the selected Cloud Provider resource and Deployment type. You can change the name of the path by clicking the field.
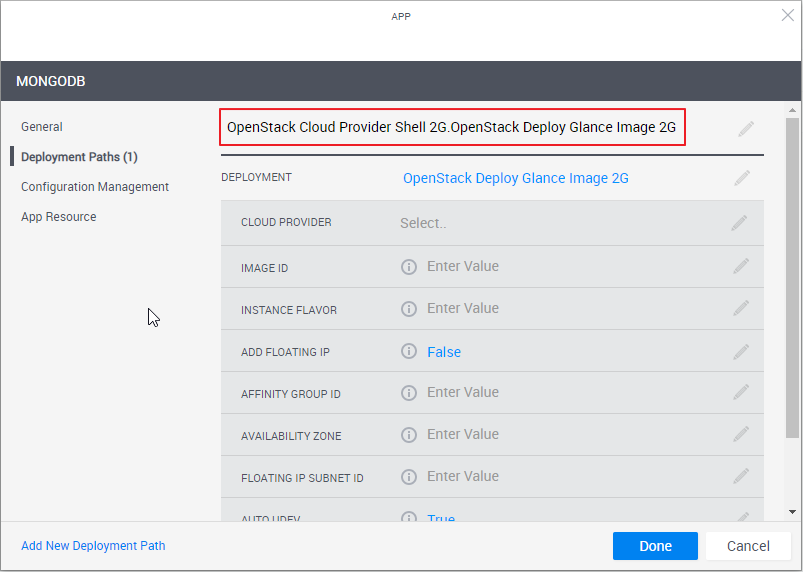
-
From the Deployment drop down list, select the deployment type.
The selected deployment type's attributes are displayed.
-
Fill in the details.
For OpenStack Deploy Glance Image 2G attributes, more...
more...
Attribute Description Cloud Provider Name of the OpenStack cloud provider resource to be used
Image ID UUID of the image to be used to create the App's Openstack instance. Can be found on Portal in Compute>Images>select the image>ID value. Instance Flavor (Optional) OpenStack instance Flavor. The instance flavor determines the CPU, memory and networking capacity of the instance. For example: "m1.tiny" or "m1.xlarge".
Can be found on Portal in Compute>Flavors>select the flavor>Flavor Name.
Add Floating IP Set to True to use a static (public) IP address to communicate with the instance from outside the virtual network. Default value is False.
In most cases the floating IP address is associated with the instance until the instance is stopped or terminated, after which the floating IP is no longer available. You can reserve a floating IP in OpenStack to ensure that the IP is available to your subscription at any time.
Affinity Group ID (Optional) UUID of the affinity group ("nova server-group") to which the instance will be associated. Affinity groups determine on which compute nodes to place instances.
Note: To support the deployment of 'all' OpenStack instances using the same hypervisor, affinity groups with the 'affinity' policy are used.
Availability Zone (Optional) Name of the availability zone to which the instance will be associated. Availability zones are used to group network nodes to enhance the availability of network resources. Floating IP Subnet ID UUID of the subnet to use for Floating IPs. Auto UDEV Enable Linux udev rules to allow new interfaces to be recognized by the OS automatically. When using Windows machines, this attribute should be set to False. Inbound Ports Semi-colon spearated list of CIDRs, ports and protocols on which to open inbound traffic from outside of the sandbox. The syntax is
[cidr:][protocol:]port-or-port-range. For example:0.0.0.0/0:tcp:80;443;udp:200-220.Default CIDR is "0.0.0.0/0". Default protocol is "tcp".
-
- To add additional deployment paths to the App template, click the Add New Deployment Path link at the bottom of the wizard and fill in the required information.
-
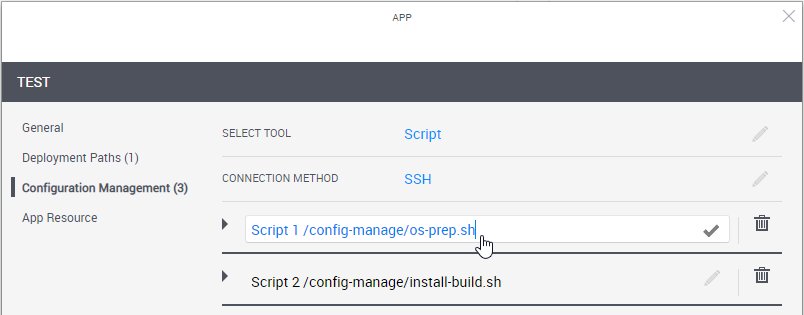
In the left pane, click Configuration Management and configure the application to be installed on the VM.
 More...
More...
Tip: To learn how to develop custom scripts and Ansible playbooks, including examples, and set up support for the desired configuration management tool, see Developing Configuration Management Scripts for Apps.
Notes:- To run configuration management on an Azure App, make sure the App's VM size is Basic_A2 or larger.
-
For configuration management operations, CloudShell uses an available Execution Server (for Ansible, it's a Linux Execution Server that has the Supports Ansible flag).
If the cloud provider resource has an Execution Server Selector configured, it will use that selector. If the selector is empty, CloudShell will use the selector defined in the appropriate Resource Manager Client >Configuration Services model (Ansible Configuration or Custom Script Configuration).
-
Execution Server selectors specified on the deployed App shell/resource are not used to execute configuration management operations.
-
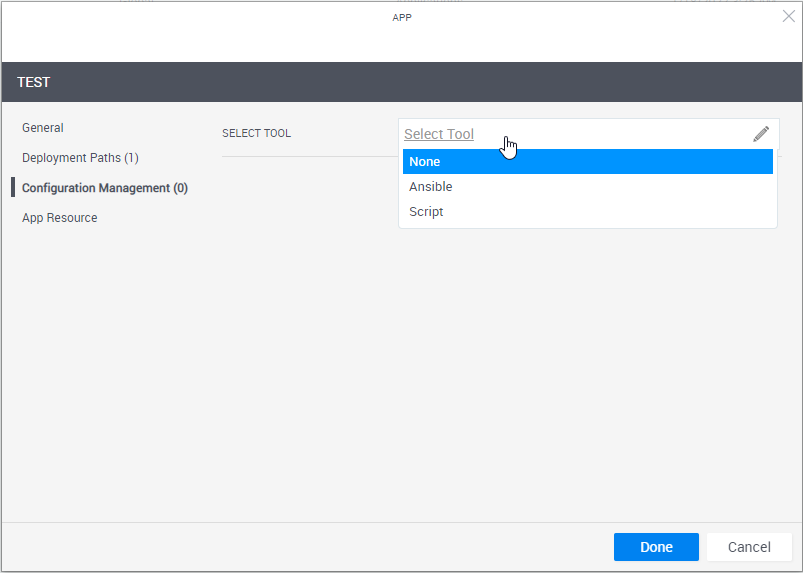
Define the script or playbook to install.
Attribute Description Select Tool Select the application's installation and configuration tool.
- None: Do not use any Configuration Management option. Use this option if, for example, the image or template already contains the application to install.
- Script: Select the custom script to run (PowerShell, bash or sh).
-
Ansible: (Intended for customers who are already using Ansible) Select the Ansible playbook to run.
Note: The playbook runs once during the Setup phase for all of the sandbox's Apps that use that playbook, after CloudShell has finished deploying their VMs. This is done both to improve performance and support cross-server logic where multiple applications need to be installed and configured in a certain way.
Note that the playbook runs once for all of the sandbox's Apps that use that playbook, after CloudShell has finished deploying their VMs.
Depending on the selection, additional options may become available.
Connection Method The method to use to connect to the VM.
Select:
- SSH if the VM has a Linux OS
-
Windows Remote Management if the VM has a Windows OS
Note: To run configuration management on a Windows VM, the VM must have WinRM enabled. For details, see Enable WinRM on Windows VMs to Support Ansible and Enable WinRM on Windows VMs to Support PowerShell Scripts.
Playbook / Script Location Details of the Ansible playbook or custom script.
-
URL: Raw URL of the Ansible playbook or ZIP file, or custom script on the online repository (GitHub, GitLab and BitBucket are supported). URL must be accessible to the Execution Servers.
Tip: The URL can accept parameters defined on the App, enabling you to test new versions of scripts without affecting consumer-ready versions. For example, you can have an App everyone is using, but if you want to test a version you're developing, simply change the value of the URL parameter in the test blueprint.- To use parameters, specify the parameter name in curly brackets (for example: {branch}).
- If the App has this parameter, CloudShell will replace the {branch} with its value during execution.
- If the parameter is missing, CloudShell will replace {branch} with emptystring.
- If you are using a global input, customers would be well advised to set a default value on the global input
 For GitHub, specify the raw URL. For example:
For GitHub, specify the raw URL. For example:
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/.../site.yml For GitLab, specify the API endpoint in the format:
For GitLab, specify the API endpoint in the format:
https://gitlab.com/api/v4/projects/{Project ID}/repository/files/testsharding%2Eyml/raw?ref=masterWhere:
-
Each special character that the file contains has to be encoded. In the example above - “%2E” is an encoded point (“.”)
-
The ref value is the branch name (master for this example)
 For BitBucket Data Center (on premise), use the following URL format:
For BitBucket Data Center (on premise), use the following URL format:
http://{datacenter server IP}/rest/api/1.0/projects/{projectKey}/repos/{repository name}/raw/testsharding.yml For BitBucket Cloud, use one of the following:
For BitBucket Cloud, use one of the following:
-
For source code files, specify the API endpoint:
https://api.bitbucket.org/2.0/repositories/{username}/{repository name}/src/{GUID- the Commit hash string} /testsharding.yml -
For download files (files residing in the repository's "Downloads" folder), specify this endpoint:
https://api.bitbucket.org/2.0/repositories/{username}/{repository name}/downloads/site.yml
Important: If the URL is private (HTTPS), the VM will need to have a valid SSL certificate. To disable the certificate check, open Resource Manager Client>Resource Families>Configuration Services (Ansible Configuration or Custom Script Configuration) and set the Verify Certificate attribute to False.
-
User/Password: (For private repositories) Access credentials or token to the script/playbook's online repository.
-
Token: (For private repositories) Access token to the script/playbook's online repository.
For GitHub and GitLab, specify the API token. For BitBucket Cloud, set the repo's "App Password" in the App template's Password field. For BitBucket Data Center, specify the personal access token.
Notes:- For Custom Script configurations: In SSH mode, only bash and sh scripts are allowed. In WinRM mode, only PowerShell scripts are allowed. WinRM over HTTPS only applies to custom scripts at this time. If WinRM is configured to run over HTTPS, the execution server will first try to run the custom script over HTTPS and then fall back to HTTP if HTTPS is unsuccessful. To prevent the fallback, set the winrm_transport parameter to ssl.
- For Ansible configurations: The Ansible playbook must be a YML or YAML file. To specify multiple playbooks or a hierarchy of an Ansible project, you can specify multiple Ansible playbooks or a ZIP package. For example:
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/QualiSystemsLab/private-repo-zip-download/master/README.zip - If a ZIP containing 2 or more playbooks is specified, CloudShell will use the playbook file titled site.yml or site.yaml. If the file is missing, the App's deployment will fail.
Inventory Groups (For Ansible) Specify the host groups for the application to be installed, separated by semicolons (;). The newly deployed VM will be associated to these groups, thus allowing plays that target these groups to run on the VM.
For example:
Servers/AppServers;Servers/DBServersParameters Parameters to be passed to the Ansible playbook or custom script. Specify the parameters and their default values.
In the blueprint or sandbox diagram, privileged users can also set the parameter to receive the value that is specified for a global input when reserving a sandbox containing the App. This is done by selecting the global input when editing the App in the blueprint or sandbox diagram. For example, a global input that specifies the build number of a product to be tested or which components of a product to install.
(For Ansible) To customize the port to be used to communicate with the VM, add the
Ansible_portparameter. Default:SSH/Port: 22/WinRM: 5985.Additional Arguments (For Ansible) Define arguments to be passed to the execution of the playbook (
Ansible-playbookcommand). For example,-vwill set verbose mode on while-fwill set the maximum number of VMs to be handled in parallel. Multiple arguments can be given, separated by spaces. For additional information on possible arguments, see the official Ansible documentation.The arguments must be specified in Resource Manager Client > Configuration Services family > Ansible Configuration model > Ansible Additional Arguments attribute.
Note: The arguments are defined globally for all Apps using Ansible.
Important: To configure Ansible to connect to certified hosts only (Linux VMs with a valid 'known_hosts' key), include the following additional arguments:
--ssh-extra-args='-o StrictHostKeyChecking=yes' -
To enable the end-user to rerun the App's configuration management on the deployed App in the sandbox, select Allow rerunning configuration management for resources deployed from the App. Once the App's deployment completes, a Rerun Configuration Management command is included in the deployed App's Application Commands pane. For details, see Run App Commands. This is useful for rolling back the App's VM to its original state.
- To enable blueprint and sandbox owners to modify the App's Configuration Management details, select Allow blueprint/sandbox owners to modify the App's Configuration Management. The following details can be modified: playbook/script, authentication details, inventory groups, and parameters. Note that the modifications only apply to the blueprint or sandbox of the instance.
- Optionally click the Add New Script/Playbook link at the bottom right to add additional custom scripts/Ansible playbooks to the App. The scripts will run in their display order, from top to bottom. You can drag scripts up or down to rearrange.
-
To change the script's alias, click the script's name and change as appropriate.
-
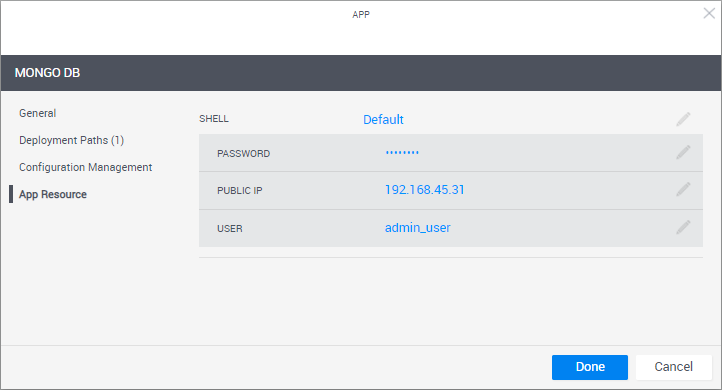
In the left pane, click App Resource to optionally set the VM's operating system user credentials (for example, to connect to the VM via RDP or SSH). You can also change the deployed App's Shell.
 More...
More...
To help sandbox end-users connect to the VM, it is recommended to include the User and Password in the blueprint's instructions. For additional information, see Add Instructions.
Attribute Description Shell The Shell on which the App's VMs are based. When an App is deployed in a sandbox, it changes into a "deployed App resource", which is based on the selected Shell. By default, the "Generic App Model" Shell is used.
Deployed Apps include a default set of commands such as Power On and Refresh IP, and the VM's User and Password attributes, as explained below.
Note: Changing the Shell might cause additional fields to become visible and you may need to enter further information.
User User defined in the App's image. The User/Password credentials are used by QualiX to create in-browser connections to the VM from within the sandbox.
Notes:- For AWS instances,make sure to set the User of a user that already exists on the Amazon machine image. For custom images, the image owner should know the credentials, while community/marketplace images have the image's credentials listed in their documentation.
- Azure VM username and password restrictions apply. For details, see Frequently asked question about Windows Virtual Machines.
- For Azure Marketplace images, CloudShell will create a user on the VM based on the User/Password credentials you specify.
- For Azure Marketplace VMs, if the user is not set, CloudShell will set adminuser as the default user name.
Password VM user's password.
Notes:- For AWS Marketplace images, leave the Password empty. The AWS shell generates a new key-pair for each sandbox, which QualiX will use to establish the in-browser connection.
- For Azure Marketplace images:
- If the password is not set, only the user name will be required. For Linux VMs, CloudShell will create an SSH key-pair to enable a secure connection.
- If the password is set, it will be displayed as asterisks (******) in the blueprint or sandbox.
-
Click Done.
The new App template is displayed in the Apps page.
