AWS Integration
The AWS deployment type integrates CloudShell with the AWS public cloud. This integration enables the deployment of CloudShell Apps in AWS. CloudShell supports deploying AWS instances from AMI (Amazon Machine Image) images.
The following diagram illustrates an AWS integration (with a local CloudShell installation) hosting two live sandboxes:
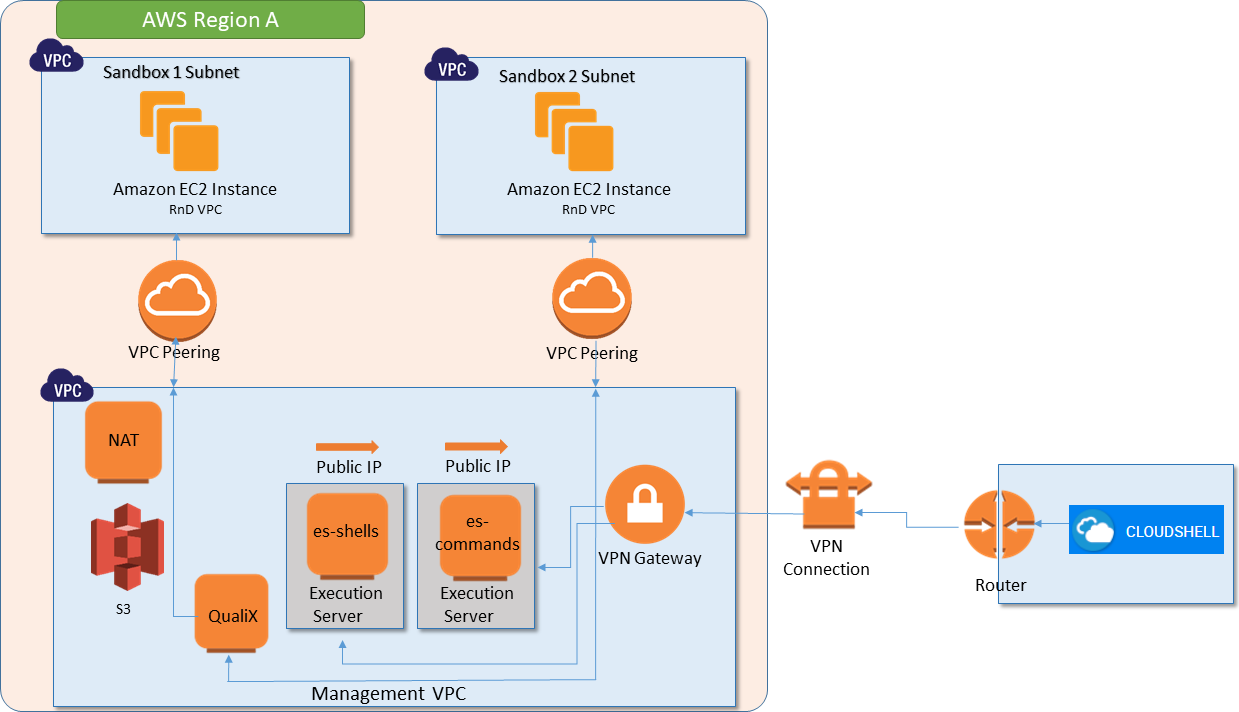
The deployment architecture in AWS requires a Management VPC to be created for each relevant AWS region. The Management VPC has 4 instances, which are always on:
- QualiX: QualiX Server used to enable in-browser RDP, Telnet and SSH access to Apps in the sandbox.
- es-shells: Execution Server to be used for the deployment and management of the AWS instances. This Execution Server has access to AWS API and is associated with an AWS IAM role.
- es-commands: Execution Server to be used for running scripts and commands on the AWS instances. This execution server is associated with an empty AWS IAM role.
- Depending on your AWS integration, either the NAT or cloudshell-server instance will be created:
- NAT: (Created in integrations where Quali Server IS NOT installed on AWS) Network address translation instance that enables internally deployed AWS instances to initiate outbound traffic to the Internet or other AWS services, while preventing the AWS instances from receiving inbound traffic from the Internet. Do not touch this instance.
- cloudshell-server: (Created in integrations where Quali Server IS installed on AWS) Empty Windows Server 2016 instance on which the Quali Server needs to be installed.
Note: Keeping these instances running at all times entails a fixed monthly rate.
Both the es-shells and es-commands Execution Servers in the Management VPC need to access the Quali Server, which is located outside of the Management VPC (on-premise, another AWS VPC or another public cloud). To allow this access, you need to configure a VPN between the Management VPC and the network in which the Quali Server resides.
When a new CloudShell sandbox with AWS EC2 Apps is starting, the out-of-the-box setup process creates a new VPC with a subnet in it. This sandbox VPC is connected to the Management VPC using a VPC Peering connection. All AWS EC2 Apps within the same sandbox are deployed in this sandbox subnet (within the Sandbox VPC). This architecture allows both QualiX Server and the Execution Servers to access the Apps in the sandbox while keeping the Apps within one sandbox isolated from Apps in other sandboxes. Note that up to 255 AWS EC2 Apps may be deployed in a single sandbox.
- AWS EC2 Apps in the same sandbox are actually on the same subnet and VPC, and can interact with each other.
- CloudShell allows sandboxes to have multiple subnets. See Subnet Connectivity.
- When the sandbox ends, the Sandbox VPC along with all its components (the subnets, the App instances and the VPC Peering) are automatically deleted by CloudShell.
- Amazon API enables you to retrieve a sandbox's VPC name using the ReservationId tag with the sandbox's ID. This can be used, for example, in real-time automation processes.
AWS installation workflow
For each AWS region you want to integrate with CloudShell, perform the following steps:
