Execution Servers - Executions Page
The Executions page displays the real time status and general information of current drivers/scripts and tests per execution server, and enables you to manage their executions.
Regarding drivers and scripts, the Executions page displays the instances of the active drivers or scripts, not the commands. For additional information, see Instance.
-
Starting with CloudShell 9.3, CloudShell runs orchestration scripts directly without needing the Python Setup & Teardown blueprint driver. This out-of-the-box behavior can be changed using the ExecutePythonOrchestrationScriptsDirectly configuration key.
-
The blueprint driver is still included with CloudShell and running orchestration scripts manually from the sandbox's Blueprint Commands pane will invoke it, creating an instance in the Executions page.
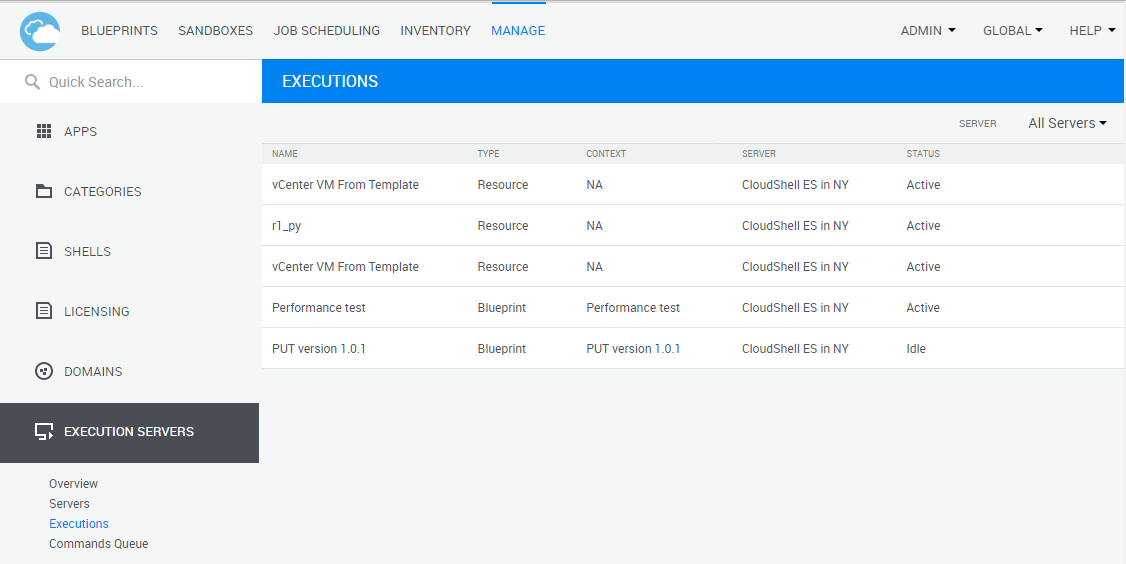
The information available for each driver or test in the Executions page includes:
| Name |
Displays the name of the resource or blueprint containing the driver, and for tests, the path of the current test. |
| Type |
Indicates the type of driver:
|
| Server | The name of the execution server running the execution. |
| Status |
Current status of the execution. For drivers:
For jobs:
|
menu icon  |
The following options are available:
For example:
|
Stopping all command executions of a specific driver instance
This procedure shuts down the command executions of a driver's instance but leaves the instance alive. This also applies to script executions.
Tip: To stop a specific command execution, in the sandbox workspace, open the appropriate commands pane and click Stop. For additional information, see Stopping commands during execution.
To stop a driver's commands:
-
In the Execution Servers page, click Executions.
The Executions view of the page is displayed.
-
Click the execution's menu button and select Stop.
The execution is stopped and removed from the page. If there are any commands in the queue for this resource, they will run now in the instance.
Note: If errors occur when attempting to stop a command or a test, please contact Quali Support at: support.quali.com. Quali Support can assist you in testing your network and in adjusting your configuration to help solve these issues..
Terminating a driver's instance or script execution
This procedure applies to Python drivers and scripts. For CloudShell Authoring drivers, see Removing a driver's instance.
Note: Driver instances may include multiple command executions while script executions only have one. For brevity, the term "instance" is used for both driver instances and script executions.
Terminating a driver's instance immediately cancels all running commands on that instance, without waiting for them to complete. Therefore, it is recommended to either stop a command or let it run its course instead of terminating.
In some cases, however, terminating an instance is required. For example, if you associate the resource or App to an execution server, but already have an instance of the driver running on a different execution server, that instance will prevent new commands from running on the resource. This is because the instance is associated to the wrong execution server and multiple driver instances of the same component cannot co-exist in CloudShell. In this case, terminating the driver instance will enable the new commands to run on the correct execution server.
- Terminating running commands may cause unexpected behavior. For example, terminating a Teardown command execution on a sandbox with Azure VMs may prevent CloudShell from deleting the sandbox's resource group and VMs from the cloud provider.
- In some cases, terminating a driver's instance in one sandbox may apply to other sandboxes if the resource is shared and is being used in different sandboxes, or in a scenario where concurrent commands are running on the resource.
To terminate a driver's instance or script execution:
-
In the Execution Servers page, click Executions.
The Executions view of the page is displayed.
-
Click the execution's menu button and select Terminate.

- In the confirmation window, click OK. If there are any commands in the queue for this resource, they will run now in a new instance.
Removing a driver's instance
This procedure applies to CloudShell Authoring drivers. For Python drivers, see Terminating a driver's instance or script execution.
In some scenarios, you may need to remove a driver's instance.
For example, if you associate the resource or App to an execution server, but already have an instance of the driver running on a different execution server, that instance will prevent new commands from running on the resource. This is because the instance is associated to the wrong execution server and multiple driver instances of the same component cannot co-exist in CloudShell. In this case, terminating the driver instance will enable the new commands to run on the correct execution server.
Note: Before you remove an Authoring driver instance, make sure you stop all of the instance's command executions and exclude the execution server on which the instance resides. To exclude an execution server, see Including/excluding execution servers.
To remove a driver instance:
-
In the Execution Servers page, click Executions.
The Executions view of the page is displayed.
-
In the row of the required execution, click the menu icon and select Remove.